Moss saves moorlands
Whether in your allotment or in horticulture, fossil peat is frequently used to improve soil quality - yet the harvesting of this substrate, which occurs in moors, is destroying their…
Take soil samples to know plants‘ spring fertilization needs
Spring is the best time to fertilize your shrubs as it promotes optimal growth with healthy foliage and abundant flowers. Well-fertilized shrubs not only improve the aesthetics of the landscape…
New species discovered: Protist parasites contribute to the stability of rainforest ecosystems
Tropical rainforests are one of the most species-rich areas on earth. Thousands of animal and plant species live there. The smaller microbial protists, which are not visible to the naked…
DFG-Project: Biodiversity, Interaction and Nitrogen Cycle in Grassland Soil
“BE-Cult” (Biodiversity Exploration by Cultivation) is a joint research initiative of ZALF and the Leibniz University of Hannover. The aim of the joint research project is to better understand nitrogen…
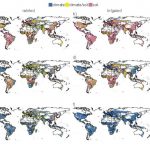
Better soil data key for future food security
Future food security depends on a variety of factors – but better soil data could substantially help improve projections of future crop yields, shows a new study from the International…
The causes of soil consumption
The soil is still under threat from urban sprawl. Small municipalities with little planning capacity and more easily accessible conurbations in particular are doing little to counter the issue. Researchers…
Researchers image roots in the ground
It's a familiar hazard of vacation time: While you're conspicuously absent, your colleagues in the office forget to water and fertilize the plants – often leaving behind nothing but a…
Beneficial here – detrimental there: European earthworms decrease species diversity in America
European earthworms are responsible for the decline in species diversity in North American Forests. Scientists from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and the Leipzig University have now…